Introduction of feature representations of the speech signal
09/10/2019 Tags: Singal_ProcessPurpose
When doing the project on speech signal processing, we need to know the different feature representations of the speech signal. Any decisions in pattern recongnition system would affect classification algorithm.
For quickly recapping the conception of features of speech signal and avoiding to forget bit and pieces of this knowledge, I recorded this relevant information in this post.
Abstract
Through more than 30 years of speech reconginizer research, many different feature representations of the speech signal have been suggested and tried. The most popular feature representation currently used is the Mel-frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCC). Another popular speech feature representation is known as Relative Spectral Transform - Perceptual Linear Prediction (RASTA-PLP). Gammatone Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (GFCC) is also one of feature representations of the speech signal.
Feature representatiion
The popular feature representation of the speech signal
Mel-frequency Cepstral Coefficients
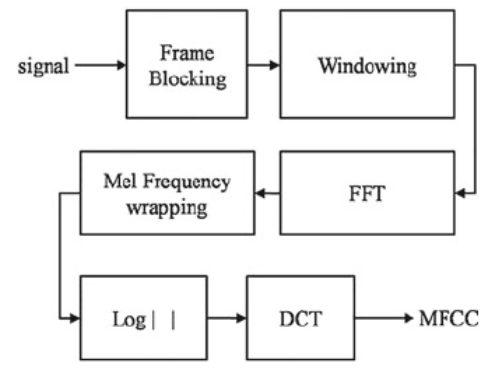
MFC is a representation of the short-term power spectrum of a sound, based on a linear consine transform of a log power spectrum on a nonlinear mel scale of frequency. The coefficients are derived from a type of cepstral representation of the audio clip.
MFCCs are commonly derived as follows:
- Take the Fourier transform of a signal.
- Map the powers of the spectrum obtained above onto the mel scale.
- Take the logs of the powers at each of the mel frequencies.
- Take the discrete cosine transform of the list of mel log powers.
- The MFCCs are the amplitudes of the resulting spectrum.
Typical MFCC features:
- 12 cepstral coefficients
- 1 delt engergy feature
Total -dimensional features
The diagrammatic MFCC block diagram
Relative Spectral Transform - Perceptual Linear Prediction
The RASTA-PLP uses bandpass filtering in the log spectral domain then RASTA filtering removes slow channel variations. To put it simply, it is a separated technique that applies a bandpass filter to the energy in each frequency subband in order to smooth over short-term noise variations and to remove any constant offset resulting from static spectral coloration in the speech channel, e.g. from a telephone lone.
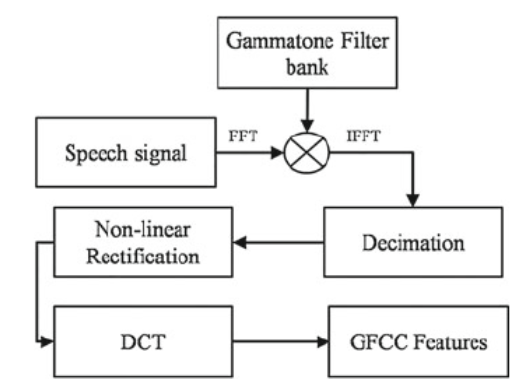
Gammatone Frequency Cepstral Coefficients
The GFCC is based on a set of Gammatone Filter banks and the speech signal is multiplied to the Gammatone filter bank in the frequency domain. In recent studies have shown very good robustness against noise and acoustic change.
The diagrammatic GFCC block diagram
=========== To be continued…. ==========
Reference
[2] GAMMATONE AND MFCC FEATURES IN SPEAKER RECOGNITION
[3] Robust Speaker Verification UsingGFCC Based i-Vectors
[4] Chapter 9: Automatic Speech Recognition
Thanks for reading! Feel free to leave the comments below or email to me. Any pieces of advice or discussions are always welcome. :)
